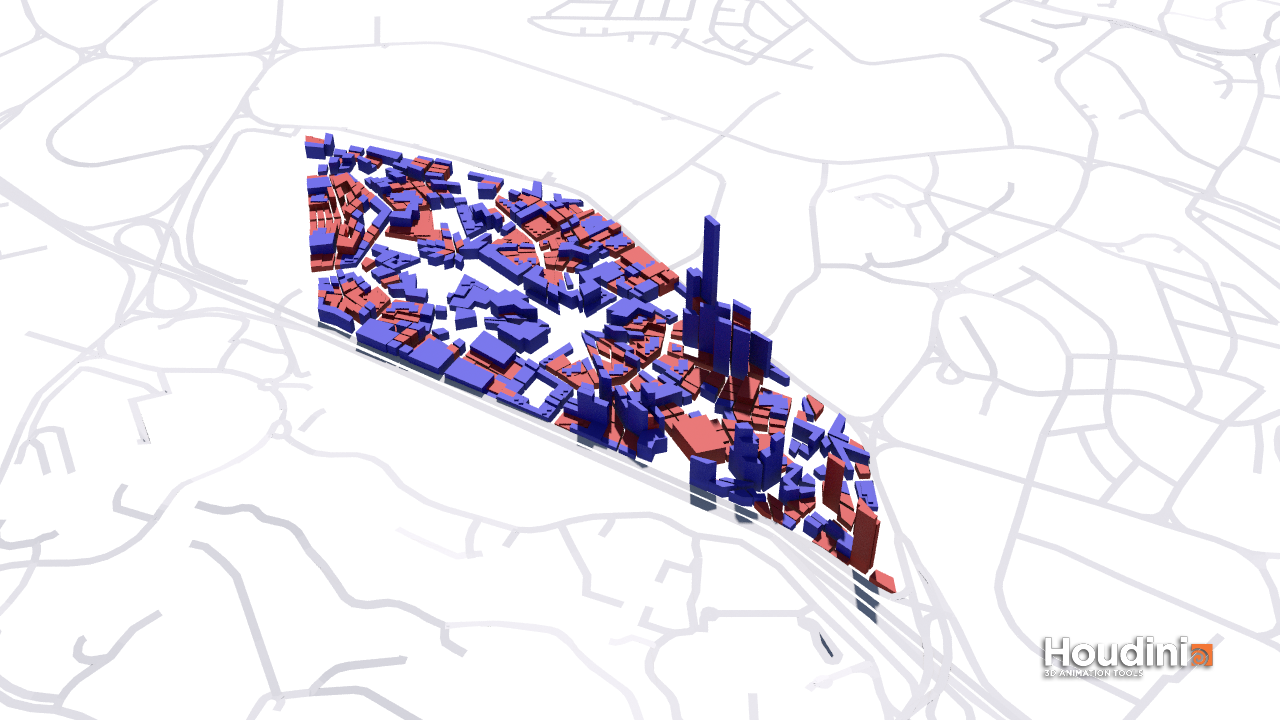
Iteration 2: “Organic” City – Mixed Urban Grain; Plot function determined by Area
In this iteration, Plots were divided into four or more until each plot reaches a certain size. Irregular and small plots were merged. Larger Parks, Industrial, and Mixed Residential-Commercial Plots were identified first, followed by other more fine-grained commercial, residential, and Industrial plots. Civic buildings were introduced into this iteration for the left-over small plots scattered around the site. They will subsequently serve as a density attractor for residential plots.
Set-up
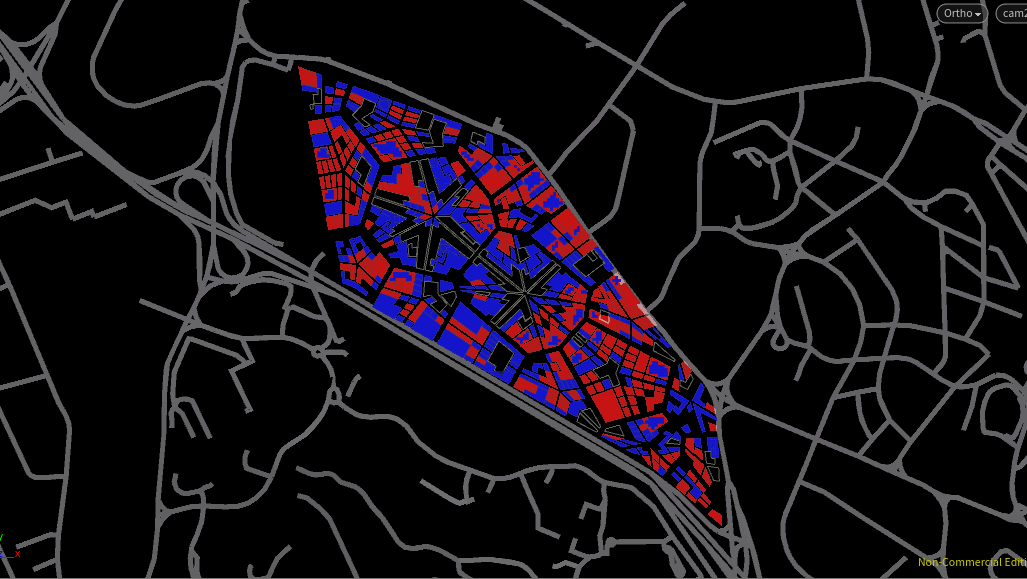
 Interestingly, the resulting program distribution created radial parks, commercial, and residential plots around the site – each with a mixed scatter of other programs.
Interestingly, the resulting program distribution created radial parks, commercial, and residential plots around the site – each with a mixed scatter of other programs.
Weighting Relative Density Calculations
To control the favourable conditions for each program, parameters are established as weights for the calculation of the relative densities
- Industrial
- Proximity to AYE (reversed): 0.015
- Proximity to MRT: 0.893
- Proximity to Central Points: 0.247
- Proximity to Arterial Roads (reversed): 0.013
- Proximity to Parks: 0.206
- Proximity to Civic Buildings: 0.015
- Commercial
- Proximity to AYE (reversed): 0.015
- Proximity to MRT: 0.514
- Proximity to Central Points: 1
- Proximity to Arterial Roads (reversed):0.013
- Proximity to Parks: 0.765
- Proximity to Civic Buildings: 0.021
- Residential
- Proximity to AYE (reversed): 1
- Proximity to MRT: 1
- Proximity to Central Points: 0.232
- Proximity to Arterial Roads (reversed): 0.869
- Proximity to Parks: 1
- Proximity to Civic Buildings: 0.807
Relative Density Calculations were weighted as above to achieve
- Denser Industrial and Commercial Buildings near AYE and Arterial Roads – Inverse for Residential due to noise
- Industrial and Residential with higher proximity to the MRT to cater to the working class
- Commercial with high proximity to the city centres
- Commercial and Residential with high proximity to the Parks
- Denser Residential where it is near a civic building
Resulting Relative Densities
The more favourable a plot is for the program, the denser the plot is – highlighted in blue in the following images.
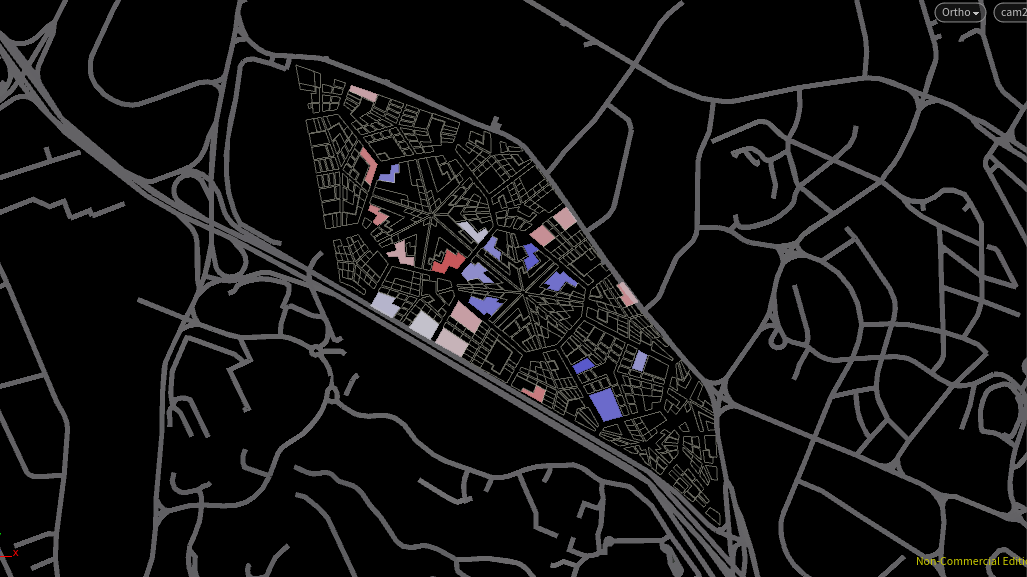 Relative Density for Industrial
Relative Density for Industrial
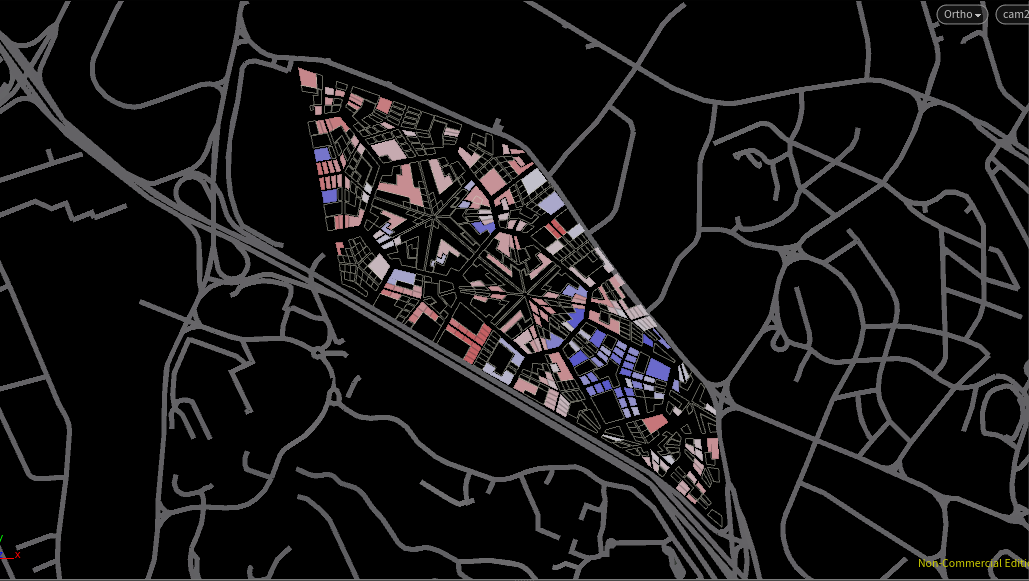 Relative Density for Commercial
Relative Density for Commercial
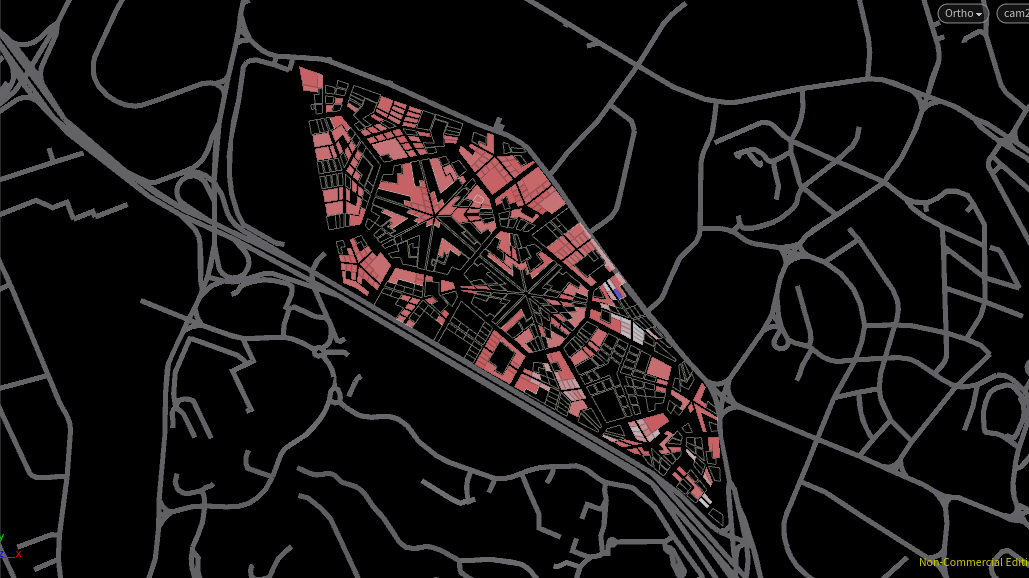 Relative Density for Residential
Relative Density for Residential
Floor Area/Head
The following floor area/head was used to generate the city massing. To accommodate the new civic program, floor area/head for residential was reduced.
- Industrial: 5sqm
- Commercial: 8sqm
- Residential: 20sqm
- Civic: 2sqm
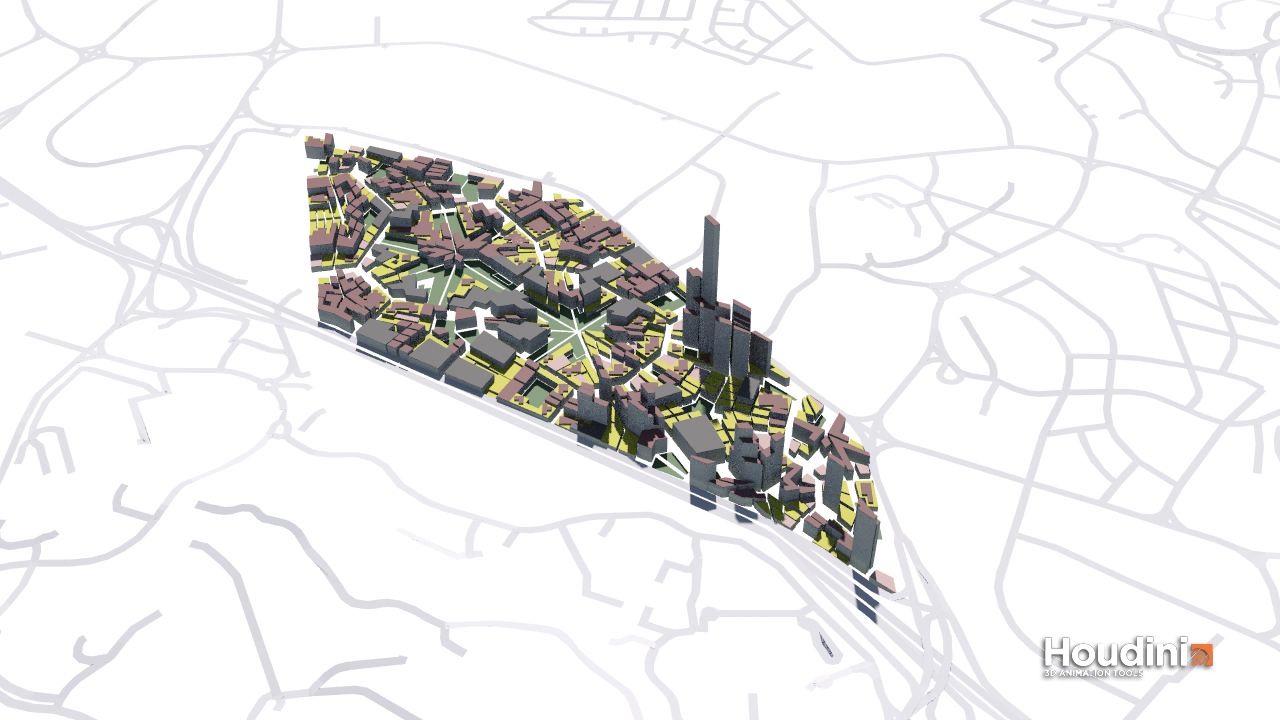
Result
The Relative Densities were compensated with its respective footprint area before finally computing number of floors required for 75 000 people.

Environment Evaluation
- Percentage Good Windows: 20.7277
- Percentage Good VF: 38.2298
- Percentage Good SF: 86.1899
- Percentage Good PR: 96.9172
- Percentage Good DF: 40.6992
- Percentage Good Building: 48.9831
In this iteration, larger building masses serve as landmarks in the sea of small scaled buildings. There is a good distribution of programs around and the varying street width and urban grain creates a overall messy but interesting urban scape. However, some street width - height ratio is too low, resulting in poor urban spaces and poor environment evaluated buildings.